Procalcitonin (PCT)
Calcitonin (CT) is a peptide hormone composed of 32 amino acids, secreted by the parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid gland. Calcitonin is metabolized in the liver and kidneys and is regulated by serum calcium levels. The main function of calcitonin is to regulate the concentration of calcium ions in the blood, working in conjunction with factors such as parathyroid hormone (PTH) and vitamin D to coordinate calcium and phosphorus metabolism in the body. The primary target organs of calcitonin are the bones and kidneys, where it mainly promotes the activity of osteoblasts, facilitating the deposition of bone salts in osteoid, and inhibits the absorption of calcium ions in the gastrointestinal tract and renal tubules, leading to a decrease in blood calcium concentration. Additionally, calcitonin can prevent the destruction of bone tissue in the body by inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts. The activity of osteoclasts is strictly regulated by calcitonin and its receptors, ensuring the complete protection of bone tissue in the body.
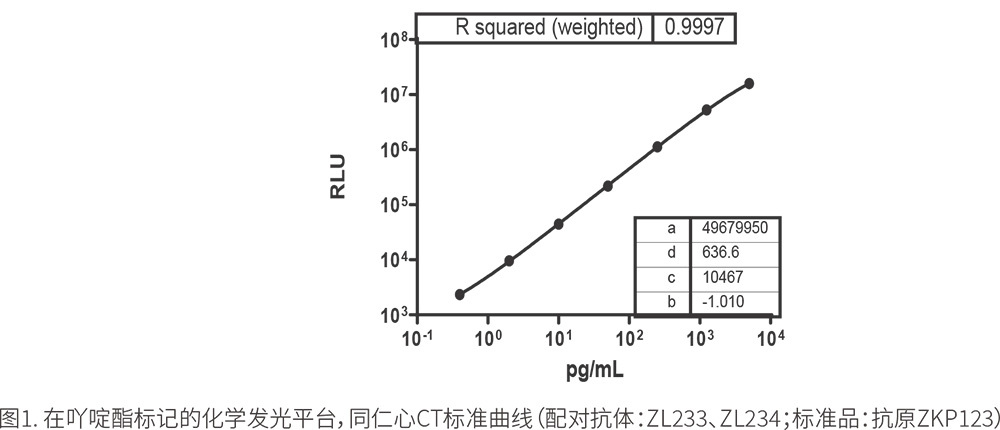
(1) Standard Curve
Using ZKP123 antigen to prepare CT standard products, the standard curve shown in Figure 1 was obtained. The curve shows that the paired antibodies ZL233 and ZL234 exhibit good linearity in the range of 0.5pg/ml to 2000pg/ml.
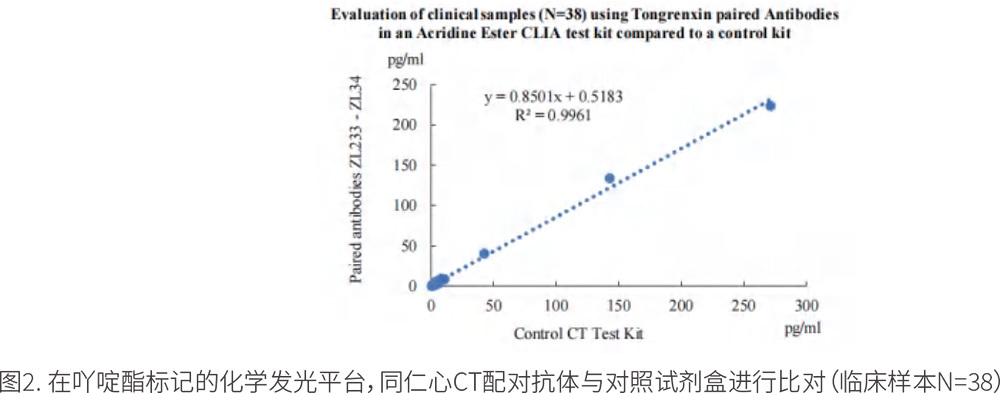
(2) Internal Evaluation of Clinical Samples
A total of 38 clinical serum samples were collected, with values assigned by an internationally recognized electrochemiluminescence reagent from a certain brand company. On the acridine ester chemiluminescence platform, our paired antibodies ZL233 and ZL234 were used to prepare the corresponding reagents (ZL233 antibody coupled with carboxyl magnetic beads, ZL234 directly labeled with acridine ester). The test results showed a very high correlation between the samples, R2=0.9961, as detailed in Figure 2.
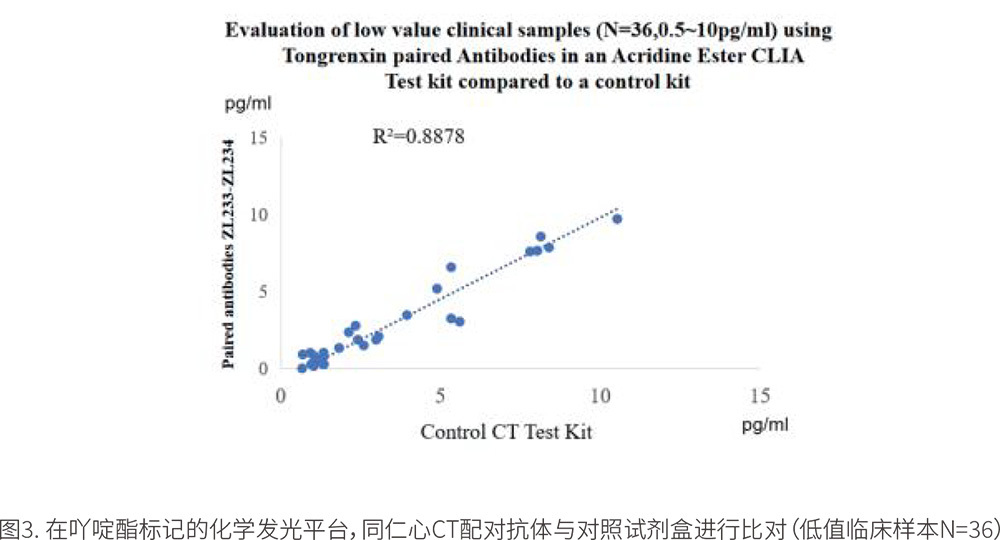
In another test of 36 low-value clinical samples, the results showed that the paired antibodies had a low-value correlation with the control reagent, R2=0.8878 (0.5pg/ml to 10pg/ml).
(3) External Evaluation of Clinical Samples
The paired antibodies ZL233 and ZL234 were distributed to three different IVD R&D laboratories to test the performance of our CT raw materials on different platforms. Due to data confidentiality requirements, these three laboratories only provided preliminary test data. Since the process has not been finely adjusted and optimized, the displayed data may not be the best. Fortunately, all three laboratories ultimately chose our paired antibodies as their preferred raw materials.
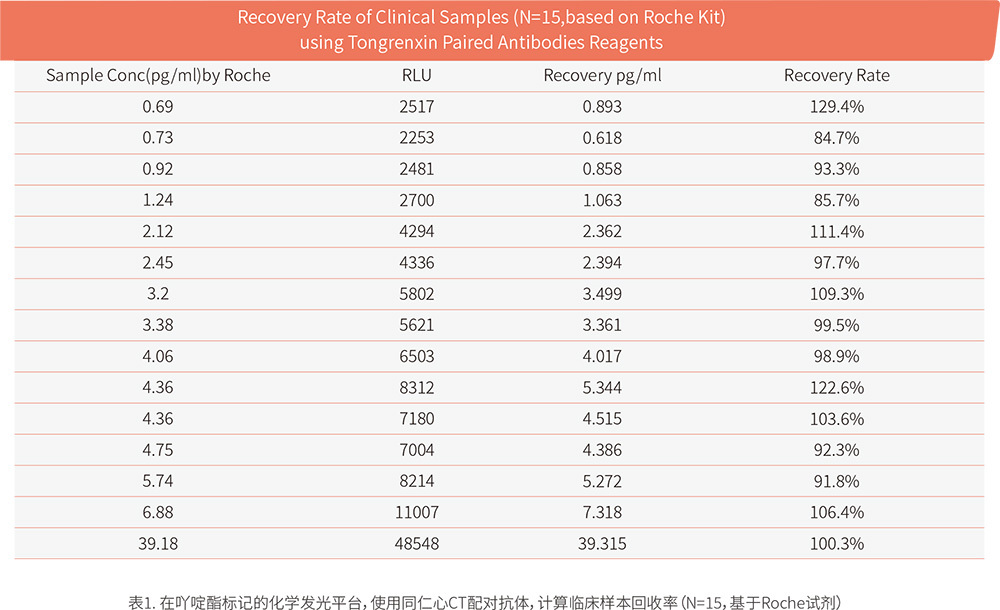
IVD R&D Laboratory 1: The data in Table 1 comes from the "Real****" client, who has been engaged in acridine ester chemiluminescence R&D for 8 years. The experiment used our paired antibodies ZL233 and ZL234. The results showed that the paired antibodies had a good recovery rate compared to the control reagent.
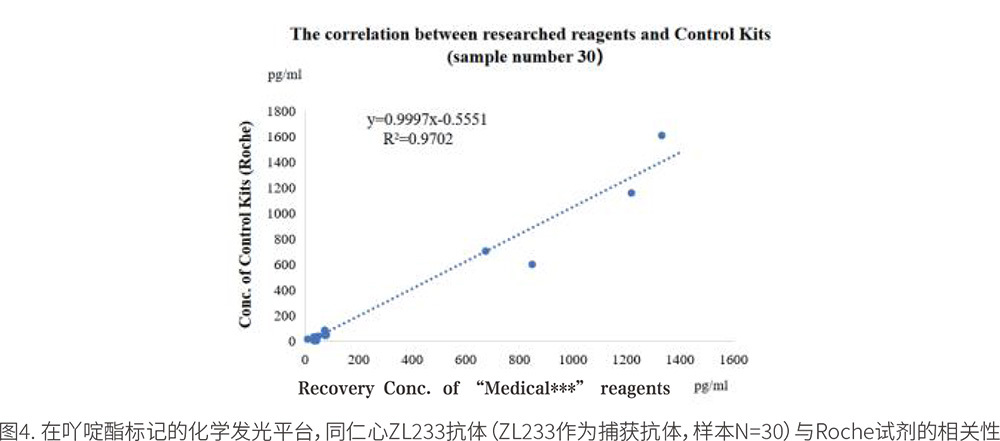
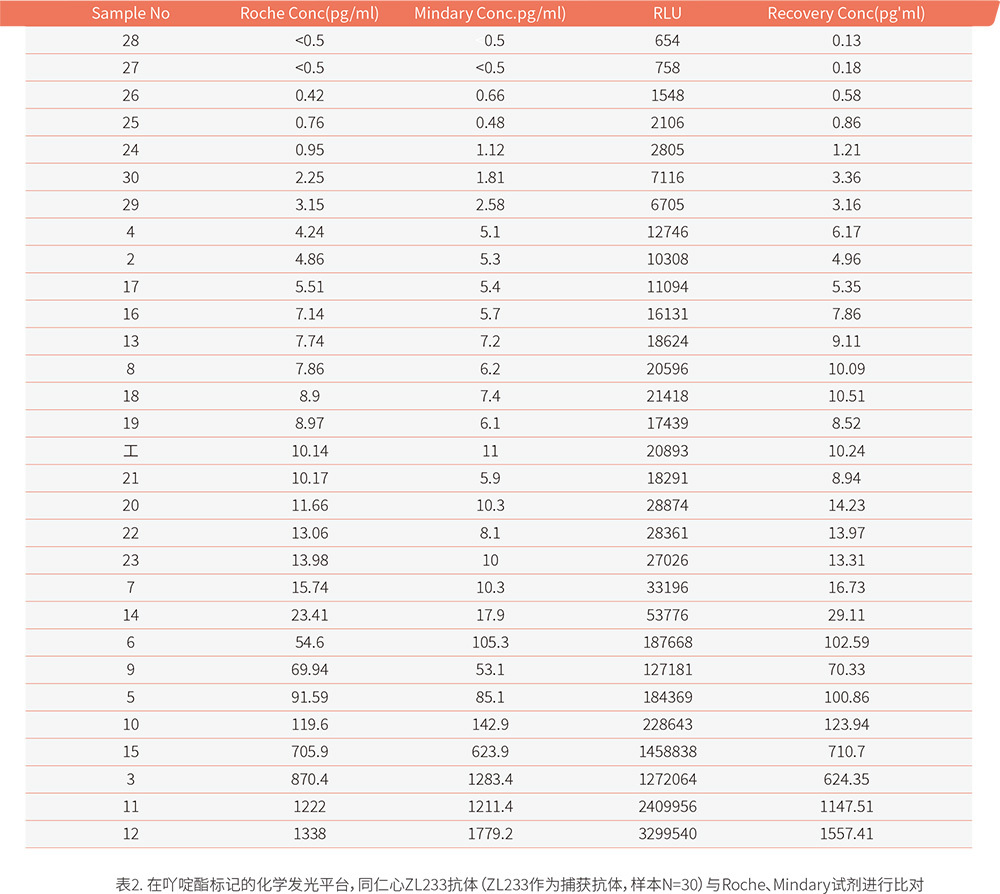
IVD R&D Laboratory 2: The data in Figure 4 and Table 2 comes from the "Medical***" client, who also conducted tests on acridine ester chemiluminescence. In the experiment, only the ZL233 antibody was selected as the capture antibody, directly coupled with carboxyl magnetic beads. The data showed that the reagent using the paired antibody ZL233 as the coating antibody had a very high correlation with the control reagent, with an R2 value of 0.9702.
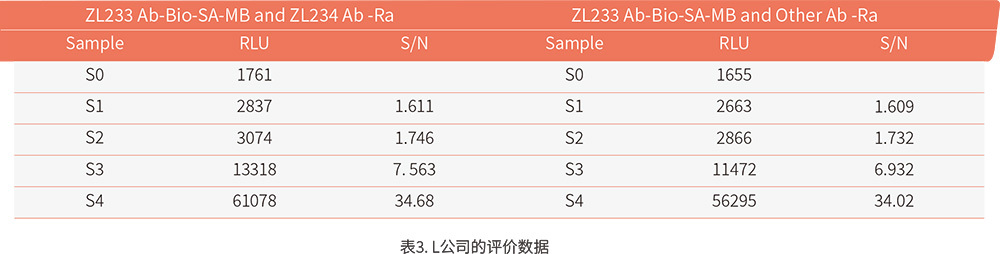
IVD R&D Laboratory 3: The data in Table 3 comes from the "L" client, who is engaged in electrochemiluminescence. In this experiment, the preliminary evaluation data showed a good response gradient, but the signal-to-noise ratio was insufficient and required further optimization of the process.
References
[1] Schou W S, Ashina S, Amin F M, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and pain: a systematic review[J]. Journal of Headache & Pain, 2017, 18(1): 34.
[2] Sekiguchi T, Shiraishi A, Satake H, et al. Calcitonin-typical suppression of osteoclastic activity by amphioxus calcitonin superfamily peptides and insights into the evolutionary conservation and diversity of their structures[J]. General & Comparative Endocrinology, 2017, 246: 294-300.
[3] Xu Lingzhi, Bao Yanfang, He Fei, et al. The effect of salmon calcitonin nasal spray on bone density and bone turnover indicators in postmenopausal osteoporosis patients[J]. Chinese Primary Health Care, 2017, 24(2): 174-177.
[4] Gao Yingjie, Gao Kun, Wang Yisheng, et al. The regulatory effect of calcitonin on osteoclast proliferation and apoptosis[J]. Chinese Tissue Engineering Research, 2008, 12(28): 5410-5413.
[5] An Yang. The effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide on apoptosis and autophagy of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts under serum starvation conditions[D].
[6] Chinese Anti-Cancer Association Thyroid Cancer Professional Committee. Expert consensus on the clinical application of serum markers for thyroid cancer (2017 version)[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2018, 45(1): 7-13.
[7] Weng Qingzhong. The diagnostic significance of procalcitonin in dilated cardiomyopathy with infection[J]. Sichuan Medical Journal, 2014, (07): 863-865.
[8]. Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Muller B. Biomarkers to improve diagnostic and prognostic accuracy in systemic infections [J]. Current opinion in critical care, 2007 Oct; 13(5): 578-85.
[9]. Gattas DJ, Cook DJ. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic test for sepsis: health technology assessment in the ICU [J]. Journal of critical care, 2003 Mar; 18(1):52-8.
[10]. Becker KL, Snider R, Nylen ES. Procalcitonin assay in systemic inflammation, infection, and sepsis: clinical utility and limitations [J]. Critical care medicine, 2008, Mar; 36(3): 941-52.



